The GI tract is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus. The hollow organs that make up the GI tract are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. The liver, pancreas, and gallbladder are the solid organs of the digestive system. The small intestine has three parts.
Pin on Edu kids
The mouth is the first part of the digestive system (gastrointestinal tract, or GI tract). When we eat, food passes down the gullet (oesophagus), into the stomach, and then into the small intestine. The small intestine has three sections – the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine and follows on from

Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Policy Function What is the stomach’s function? Your stomach’s purpose is to digest food and send it to your small intestine. It has three functions: Temporarily store food. Contract and relax to mix and break down food. Produce enzymes and other specialized cells to digest food. How does the stomach work with the rest of the GI tract?
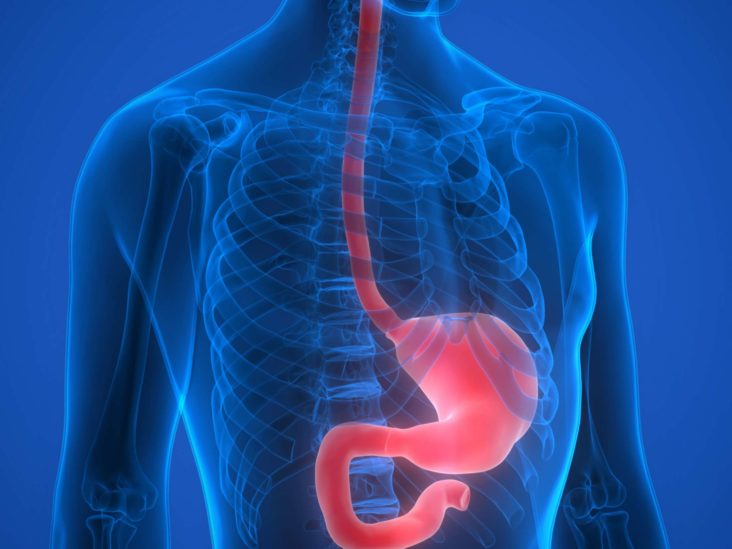
Source Image: medicalnewstoday.com
Download Image
The Digestive System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 2 | Serous membrane, Digestive system, Gastric juice
Nov 2, 2023Functions of the digestive system Trigger and initiation. The function of the digestive system truly begins within the brain.Whenever the body’s energy stores (i.e. blood glucose, protein, or fat stores) fall below a set point, the hunger centres of the hypothalamus are activated. These centres regulate satiety (fullness) and appetite in order to maintain energy homeostasis.
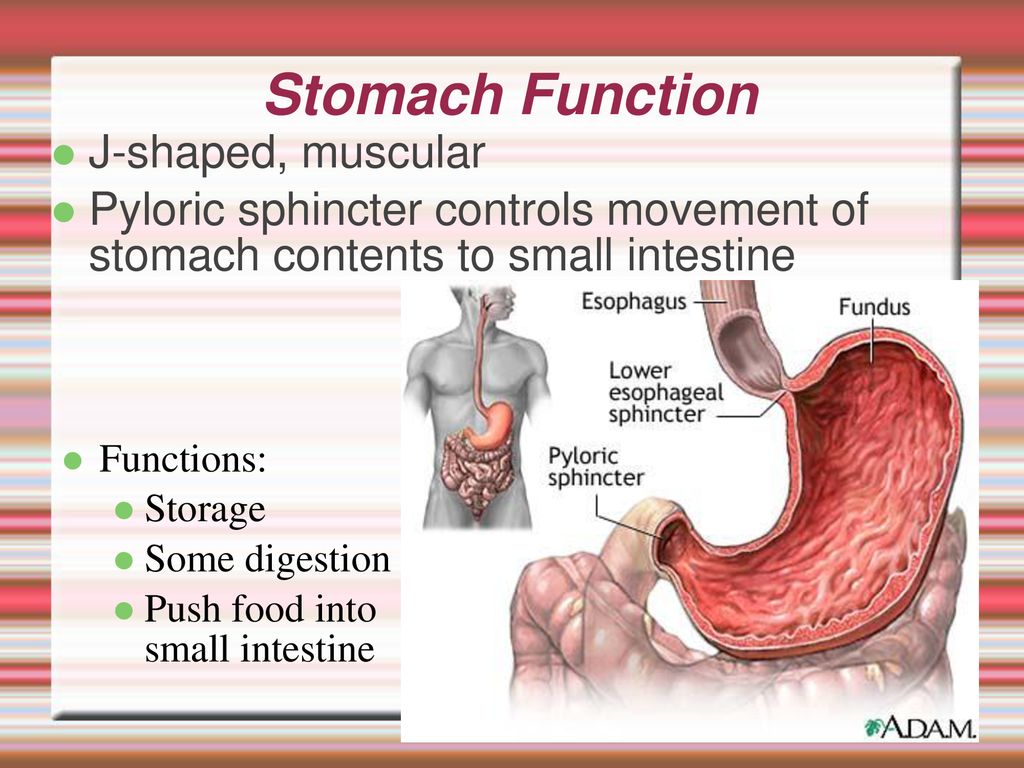
Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
The Function Of Sphincters In The Digestive Tract Is:
Nov 2, 2023Functions of the digestive system Trigger and initiation. The function of the digestive system truly begins within the brain.Whenever the body’s energy stores (i.e. blood glucose, protein, or fat stores) fall below a set point, the hunger centres of the hypothalamus are activated. These centres regulate satiety (fullness) and appetite in order to maintain energy homeostasis.
The stomach (Figure 18.4.4 18.4. 4 is a J-shaped organ that is joined to the esophagus at its upper end and to the first part of the small intestine (duodenum) at its lower end. When the stomach is empty of food, it normally has a volume of about 75 mL. However, it can expand to hold up to about a liter of food.
6.2 – Digestive System. – ppt download
Oct 13, 2023The primary job of the LES is to keep the acid and food in your stomach from coming back up into your throat. A weak LES is a common cause of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), in which the esophagus is irritated by stomach acid or bile.
The Stomach – Gastrointestinal Society
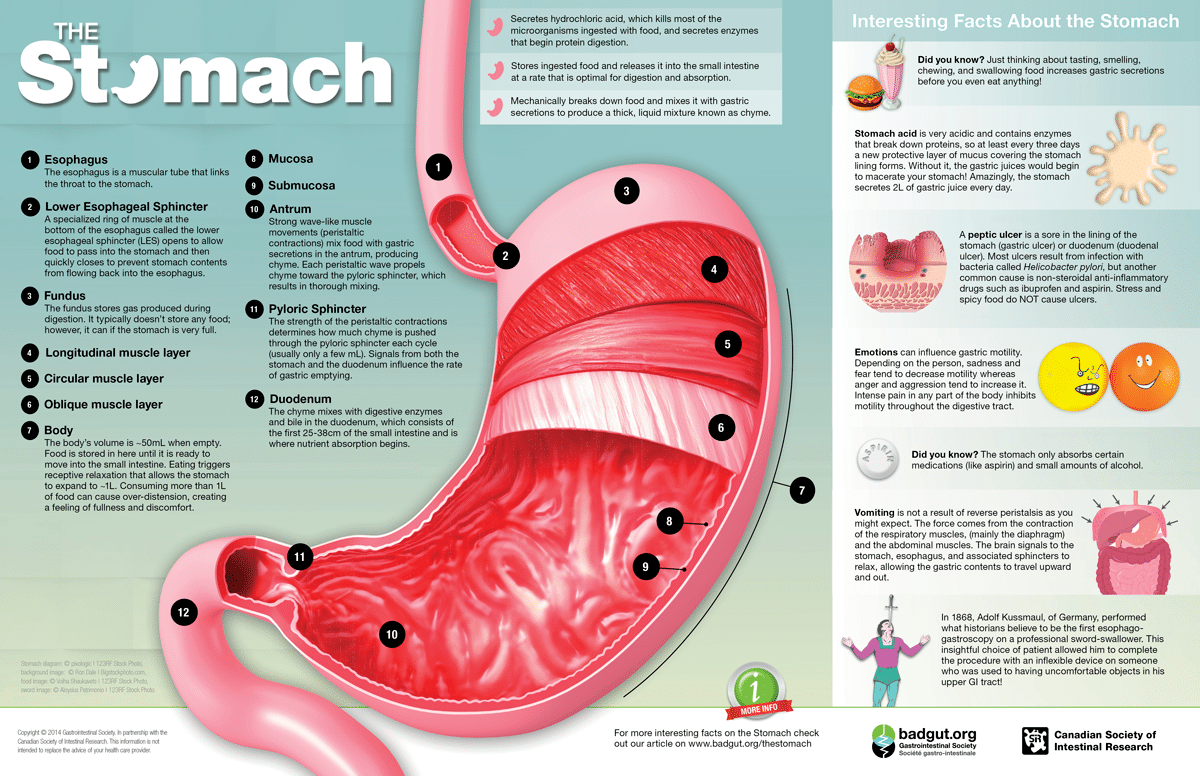
Source Image: badgut.org
Download Image
Sphincters: Where They’re Found and Purpose
Oct 13, 2023The primary job of the LES is to keep the acid and food in your stomach from coming back up into your throat. A weak LES is a common cause of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), in which the esophagus is irritated by stomach acid or bile.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-165564610-5a60a646c7822d0037df638b.jpg)
Source Image: verywellhealth.com
Download Image
Pin on Edu kids
The GI tract is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus. The hollow organs that make up the GI tract are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. The liver, pancreas, and gallbladder are the solid organs of the digestive system. The small intestine has three parts.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
The Digestive System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 2 | Serous membrane, Digestive system, Gastric juice
Policy Function What is the stomach’s function? Your stomach’s purpose is to digest food and send it to your small intestine. It has three functions: Temporarily store food. Contract and relax to mix and break down food. Produce enzymes and other specialized cells to digest food. How does the stomach work with the rest of the GI tract?

Source Image: in.pinterest.com
Download Image
An In-Depth Look at Human Digestion – Shield Nutraceuticals
Mar 17, 2023The esophagus is a portion of the digestive system connecting the pharynx to the stomach, allowing the passage of food for digestion. The esophagus measures approximately 25 cm long in a mature adult and begins at the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage (C6 level), descending in the posterior mediastinum through the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm and terminating at the stomach (T11

Source Image: shieldnutra.com
Download Image
The function of the digestive system | Mouth, Stomach, Pancreas, Intestine
Nov 2, 2023Functions of the digestive system Trigger and initiation. The function of the digestive system truly begins within the brain.Whenever the body’s energy stores (i.e. blood glucose, protein, or fat stores) fall below a set point, the hunger centres of the hypothalamus are activated. These centres regulate satiety (fullness) and appetite in order to maintain energy homeostasis.

Source Image: online-learning-college.com
Download Image
Sphincter Muscle | Definition & Function | Study.com
The stomach (Figure 18.4.4 18.4. 4 is a J-shaped organ that is joined to the esophagus at its upper end and to the first part of the small intestine (duodenum) at its lower end. When the stomach is empty of food, it normally has a volume of about 75 mL. However, it can expand to hold up to about a liter of food.

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Sphincters: Where They’re Found and Purpose
Sphincter Muscle | Definition & Function | Study.com
The mouth is the first part of the digestive system (gastrointestinal tract, or GI tract). When we eat, food passes down the gullet (oesophagus), into the stomach, and then into the small intestine. The small intestine has three sections – the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine and follows on from
The Digestive System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 2 | Serous membrane, Digestive system, Gastric juice The function of the digestive system | Mouth, Stomach, Pancreas, Intestine
Mar 17, 2023The esophagus is a portion of the digestive system connecting the pharynx to the stomach, allowing the passage of food for digestion. The esophagus measures approximately 25 cm long in a mature adult and begins at the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage (C6 level), descending in the posterior mediastinum through the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm and terminating at the stomach (T11